Last June tech start-up KnuEdge emerged from stealth mode to begin spreading the word about its new processor and fabric technology that’s been roughly a decade in the making. It’s nice to have patient capital, a rare commodity for startups these days. The company contends its KNUPATH Hermosa processor with 256 DSP cores and its Lambda fabric will bring performance, scalability, energy, and programmability advantages over CPUs, GPUS, and FPGAs to a wide swath of machine learning applications. The first commercial boards – code named Mavericks – are expected around March this year.
Founded in the 2005 timeframe by Daniel Goldin, the long time NASA administrator, KnuEdge has raised roughly $100M no doubt stemming from investor confidence in Goldin’s extensive technology creation and delivery history. Goldin and company believe their investors’ patience is about to start paying off. KnuEdge has two business units, KNUPATH focused on hardware accelerators based on Hermosa and Lambda technology, and KnuVerse, focused on voice and face recognition systems. The latter, said Steve Cumings, CMO, KnuEdge, has customers in the government sector. Company revenues are somewhat north of $20 million so far.
Broadly, KnuEdge’s view is that a highly scalable processor in a single socket is handicapped in addressing growing machine learning and large-scale computing challenges. In contrast, the company’s Lambda Fabric enables a large number of “KNUPATH Hermosa processors to be interconnected in low latency, high throughput mesh for massively parallel processing which is well suited for application needs that will drive the compute engines of the future.”
This isn’t exactly a new idea. The Hermosa chip and Lambda technology will enter the market amid a gush of machine learning technologies all striving to advance data-driven science and enterprise data analytics. Indeed the emergence of heterogeneous computing architectures relying on a variety of accelerator engines is a key feature of today’s computing landscape. Given Goldin’s remarkable achievements at NASA it should be interesting to watch KnuEdge’s progress.
Early developer boards with two Hermosa chips have been available for some time. Volume sales of individual chips are planned to begin in January followed by the Mavericks offering, a PCIe board with four Hermosa chips, towards the end of the quarter.
Presented as a “neural computing” approach, the KNUPATH architecture actually attempts to mimic nervous system communication more than brain-inspired spiky neuron ‘inference logic’ (discussed further below).
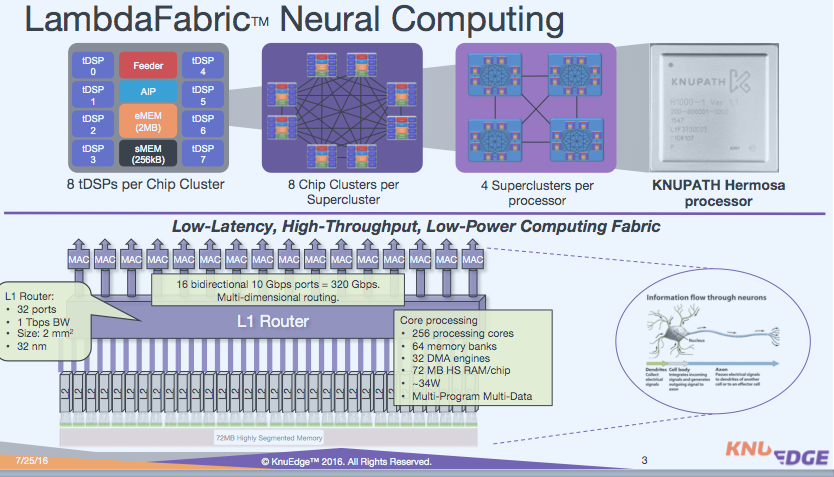 Patrick Patla, senior vice president and general manager of KNUPATH and a former AMD executive, said, “What’s unique about Hermosa’s 256 DSP cores is that they are hooked together at a central part of the processor with a router that has 16 ports. Using the Lambda fabric, it’s possible, at least theoretically, to scale to 500,000 Hermosa processors.
Patrick Patla, senior vice president and general manager of KNUPATH and a former AMD executive, said, “What’s unique about Hermosa’s 256 DSP cores is that they are hooked together at a central part of the processor with a router that has 16 ports. Using the Lambda fabric, it’s possible, at least theoretically, to scale to 500,000 Hermosa processors.
“We are a data flow machine. So you push data through the system and can have the calculation and different algorithms change on the fly. We are different than a GPU accelerator in that they use a SIMD architecture. We use multiple programs, multiple data, so on our 256 cores we could have 256 separate algorithms running. You would push data through those algorithms and then you have hits on the data at different hit rates based on the algorithms and you can tune and resend algorithms to those DSPs through packets,” explained Patla.
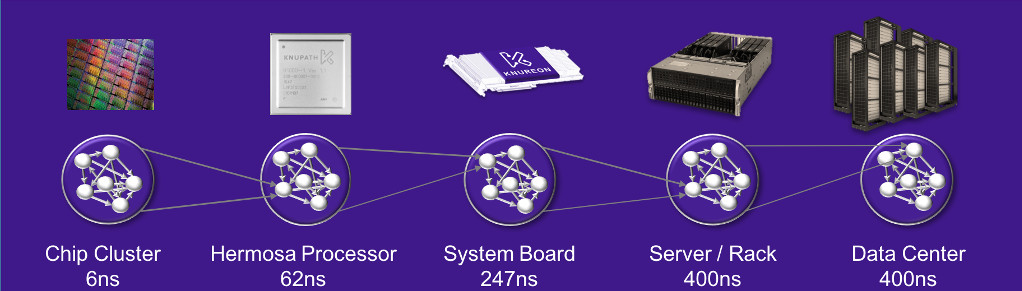
“Basically the packets that we send through the Lambda network are what allows the programming of the DSP, so packets deliver the program, the algorithm, and then bring the payload, and push the data through it. Not only are you getting all the data and the operating instructions with each packet, but each core also knows the next destination for that information so it’s extremely efficient.” One result is very low latency at various systems levels (see diagram below).
Patla also contrasted Hermosa’s ease of use with emerging brain-inspired neuromorphic chips such as IBM’s TrueNorth, which uses “spiking neuron” architecture.
“Spiky algorithms are notoriously difficult to program. Commonly they are trained on other networks first and then moved onto the neuromorphic chip so the actual software side of that is different,” he said.
As noted earlier the Hermosa-Lambda architecture emulates neuronal connectivity more than brain processing. “If you look at the different neuron-based approaches, our inspiration really gives you lots of little engines – that’s the background of the DSP cores, what we affectionately sometimes call tDSPs or tiny DSPs,” said Patla. Reliance on familiar DSP architecture eases programming.
“Our tools sit on a C/C++ library set on top of LLVM (compiler). And everybody is familiar with OpenCL as well as OpenMPI which is very comfortable in our architecture,” said Patla. The Hermosa/Lambda architecture also supports NUMA (non uniform memory access) and each processor has memory directly (72MB) on it. “Much of the advantage is the dataflow but also all the advantages of common programming techniques for anybody that has worked on OpenMPI. Many of the other [neuromorphic] architecture require a different set of tools.”

KnuEdge has had a software developer kit out for “quite some time” and it is already in the hands of many developers, according to Patla.
It all sounds great. In April KnuEdge will hold a Hermosa developers’ conference at UCSD as well as a “heterogeneous neural network conference” in partnership with UCSD for the development of next generation algorithms that can take advantage of new architectures such as Hermosa. Patla said performance benchmarks for chip will be forthcoming with the release of the commercial product; it seems like the developer conference would be a good place to do so, but he wouldn’t specify when beyond the first half of the year.
“Right now, as you would imagine, we are in the labs with our SDKs and final verification of those commercial systems as we are tuning and bringing all of our code to the processors. In the future we’ll show configurations of 4, 8, 12, 16, Hermosas together to show the scalability of the Lambda fabric. When Steve talked about mimicking the nervous systems it really is about our connectivity and the fact that when you add more Hermosas to the network, we continue to scale because with every socket you are adding more memory as well. Each processor has 72MB of onchip memory that is sufficient for the programming of our kinds of algorithms and the workload we are trying to tackle.”
 Currently the chip is being fabbed by GLOBALFOUNDARIES on the 32nm process. “It’s a well behaved chip where these 256 cores and fabric and everything lives in a 35-watt part,” said Patla.
Currently the chip is being fabbed by GLOBALFOUNDARIES on the 32nm process. “It’s a well behaved chip where these 256 cores and fabric and everything lives in a 35-watt part,” said Patla.
The KNUPATH folks believe Hermosa has the potential to meet a wide variety of machine-learning kinds of applications performed in heterogeneous computing environments as well as an opportunity to replace existing approaches to those applications.
‘We have a demo on the website that compares us to the most current NVIDIA card and we have a 2.5x performance. It is very interesting that a video card isn’t very good at video compression that we are good at because of the parallelism of communication we handle across the memory. So that’s one of the spaces we’ll be aiming at. And of course it will also find its way into many of the single board computer spaces because at 35 watts and the ability to do signal processing and such fine grained computing we actually expect it to replace many FPGAs in a lot of environments.”
Patla argues Hermosa/Lambda’s flexibility is a major benefit and door opener – one could divvy the chips up and have a multipurpose SOC instead of dedicating it to just one task. He used a video analysis application as an example of flexibility and reprogrammability.
“You can reprogram a core by just delivering a new packet. For example, if you were doing video analysis and were searching within videos, you could be looking for ball caps. You could have all the different algorithms looking at ball caps and you could just all of a sudden reprogram and divide the chip and have 25 percent of the chip looking for red ball caps and 25 percent looking for blue caps. You could flip to four different algorithms in nanoseconds. Then when you have high hit rates and you realize the one you are really looking for, and you could say OK now all care about our green ball caps and that algorithm would propagate against all the cores and you’d be able to take your throughput up. It’s very fast, very flexible,” he said.
At SC16, the KNUPATH team was busily evangelizing. Patla said they talked to a number of cloud providers as well as national labs that expressed interest to the point that he is expecting some new workloads to emerge.
There’s still much to do. Patla ticked off desirable milestones for 2017 – getting out of the lab, showcasing a couple of commercial customers and workloads, integrating the many machine learning frameworks, making sure Hermosa-based systems get into the cloud somewhere for development and production purposes, to name but a few.