In this regular feature, HPCwire highlights newly published research in the high-performance computing community and related domains. From parallel programming to exascale to quantum computing, the details are here.
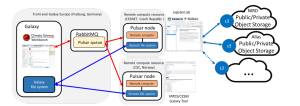
Reproducible cross-border high performance computing for scientific portals
An international team of researchers from the University of Tartu (Estonia), the University of Oslo (Norway), and the University of Iceland (Iceland) developed a software solution that allows “scientists to use cross-border cloud and HPC resources through web portals while achieving reproducibility using containers and workflow automation.” In this paper, researchers state that the solution supports job submissions from Galaxy and PlutoF portals to HPC systems. To create the solution, scientists developed “a robot user at each HPC facility for each group of users, so that user portals submit jobs as this robot user. On the HPC side, each robot user is associated with a user group to which a specific quota is assigned and managed.” The proposed solution would provide access to users needing HPC resources from one country to another (e.g., Finland to Sweden).
Authors: Kessy Abarenkov, Anne Fouilloux, Helmut Neukirchen, and Abdulrahman Azab
SCALSALE: Scalable SALE Benchmark Framework for Supercomputers
Israeli researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Nuclear Research Center, Israel Atomic Energy Commission, Israel Institute of Technology, and Tel Aviv University introduced a scalable benchmark framework based on the SALE scheme called SCALSALE. SCALSALE was developed to “provide a simple, flexible, scalable infrastructure that can be easily expanded to include multi-physical schemes while maintaining scalable and efficient execution times.” With SCALSALE, researchers hope to bridge the gap between simplified benchmarks and scientific applications. In this paper, researchers detail how they implemented SCALSALE “in Modern Fortran with simple object-oriented design patterns and supported by transparent MPI-3 blocking and non-blocking communication that allows such a scalable framework.” They demonstrated the use of SCALSALE with the “multibounded representative Sedov-Taylor blast wave problem and compared it to the well-known LULESH benchmark using strong and weak scaling tests.” The framework is publicly available on Github: https://github.com/Scientific-Computing-Lab-NRCN/ScalSALE.
Authors: Re’em Harel, Matan Rusanovsky, Ron Wagner, Harel Levin, and Gal Oren
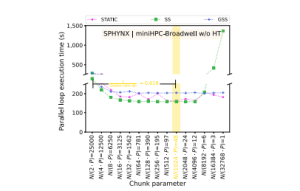
Automated scheduling algorithm selection and chunk parameter calculation in OpenMP
Switzerland researchers from HPE’s HPC/AI EMEA Research Lab and the department of mathematics and computer science at the University of Basel developed Auto4OMP. In this open access paper published by the IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems journal, researchers introduced Auto4OMP, which is a new “approach for automated load balancing of OpenMP applications.” The approach is meant to “address the scheduling algorithm selection problem in OpenMP applications.” To tackle the problem, researchers developed Auto4OMP with “a new expert chunk parameter and three new scheduling algorithm selection methods: RandomSel, ExhaustiveSel, and ExpertSel for OpenMP.” Researchers detailed their analysis of Auto4OMP’s performance and the results of their evaluation performed “on five applications, executed on three multi-core architectures to test six research hypotheses.” Results of the experiments demonstrated “that Auto4OMP improves applications performance by up to 11% compared to LLVM’s schedule(auto) implementation and outperforms manual selection. Auto4OMP improves MPI+OpenMP applications performance by explicitly minimizing thread- and implicitly reducing process-load imbalance.”
Authors: Ali Mohammed, Jonas H. Müller Korndörfer, Ahmed Eleliemy, and Florina M. Ciorba
The future of quantum computing with superconducting qubits
In this paper by a team of IBM researchers from IBM Quantum and IBM T.J. Watson Research Center in New York, researchers offer a “perspective of the future of quantum computing focusing on an examination of what it takes to build and program near-term superconducting quantum computers and demonstrate their utility.” Researchers argue that achieving computation advantage in the near future is “possible by combining multiple QPUs through circuit knitting techniques, improving the quality of solutions through error suppression and mitigation, and focusing on heuristic versions of quantum algorithms with asymptotic speedups.” However, researchers add, for this “to happen, the performance of quantum computing hardware needs to improve and software needs to seamlessly integrate quantum and classical processors together to form a new architecture that we are calling quantum-centric supercomputing.”
Authors: Sergey Bravyi, Oliver Dial, Jay M. Gambetta, Dario Gil, Zaira Nazario
 HFBN: an energy efficient high performance hierarchical interconnection network for exascale supercomputer
HFBN: an energy efficient high performance hierarchical interconnection network for exascale supercomputer
In this paper by a team of researchers from Green University of Bangladesh (Bangladesh), King Faisal University (Saudi Arabia), and the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (Japan), researchers provide a new interconnection network for supercomputers. As supercomputers require a thousand times “performance improvement over the petascale computers and energy efficiency has attracted as the key factor for to achieve exascale system.” For example, “Fugaku supercomputer used Tofu interconnect with 7,299,072 cores and can achieve about 415PFLOPS requiring about 28,335kW power usage.” In this open access paper published in IEEE Access, researchers provide an overview of their “redesigned new energy efficient interconnection network that mitigates the problems of high power consumption, longer wiring length, and low bandwidth issues.” Compared to the Tofu network, “HFBN can obtain about 87.26% better energy efficiency with uniform traffic, about 86.32% with perfect shuffle traffic, and about 92.98% with the bit-compliment traffic at the zero load latency,” the researchers wrote.
Authors: Faiz Al Faisal, M. M. Hafizur Rahman, and Yasushi Inoguchi
A team of Texas researchers from Rice University, West Texas A&M University, and ThirdAI Corp., an artificial intelligence startup company, introduced Random Offset Block Embedding Array (ROBE). Researchers created ROBE as “a low memory alternative to embedding tables, which provide orders of magnitude reduction in memory usage while maintaining accuracy and boosting execution speed.” According to the researchers, ROBE is an approach to “improving both cache performance and the variance of randomized hashing…” In this paper, researchers demonstrated they can “train DLRM models with the same accuracy while using 1000× less memory.” In addition, a “1000× compressed model directly results in faster inference without any engineering effort.” Notably, researchers trained a “DLRM model using ROBE Array of size 100MB on a single GPU to achieve AUC of 0.8025 or higher as required by official MLPerf CriteoTB benchmark DLRM model of 100GB while achieving about 3.1× (209%) improvement in inference throughput.”
Authors: Aditya Desai, Li Chou, and Anshumali Shrivastava
Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data
 In this paper by an international, multidisciplinary team of researchers from the Technical University of Munich (Germany), Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST) (Germany), Caltech (California), Los Alamos National Laboratory (New Mexico), University of Maryland, College Park, (Maryland), and Quantum Science Center (Tennessee), the authors provided a detailed analysis of “generalization performance in quantum machine learning (QML) after training on a limited number N of training data points.” Researchers demonstrated “highly general theoretical bounds on the generalization error in variational QML: The generalization error is approximately upper bounded by √T/N.” In this open access article published in Nature Communications, researchers also demonstrated that “classification of quantum states across a phase transition with a quantum convolutional neural network requires only a very small training data set.” Researchers believe that their work also can be applied to learning quantum error correcting codes or quantum dynamical simulation applications.
In this paper by an international, multidisciplinary team of researchers from the Technical University of Munich (Germany), Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST) (Germany), Caltech (California), Los Alamos National Laboratory (New Mexico), University of Maryland, College Park, (Maryland), and Quantum Science Center (Tennessee), the authors provided a detailed analysis of “generalization performance in quantum machine learning (QML) after training on a limited number N of training data points.” Researchers demonstrated “highly general theoretical bounds on the generalization error in variational QML: The generalization error is approximately upper bounded by √T/N.” In this open access article published in Nature Communications, researchers also demonstrated that “classification of quantum states across a phase transition with a quantum convolutional neural network requires only a very small training data set.” Researchers believe that their work also can be applied to learning quantum error correcting codes or quantum dynamical simulation applications.
Authors: Matthias C. Caro, Hsin-Yuan Huang, M. Cerezo, Kunal Sharma, Andrew Sornborger, Lukasz Cincio, and Patrick J. Coles
Do you know about research that should be included in next month’s list? If so, send us an email at [email protected]. We look forward to hearing from you.