Sept. 27, 2022 — Quantinuum President and COO Tony Uttley announced three major accomplishments during his keynote address at the IEEE Quantum Week event in Colorado last week.

The three milestones, representing actionable acceleration for the quantum computing eco-system, are: (i) new arbitrary angle gate capabilities on the H-series hardware, (ii) another QV record for the System Model H1 hardware, and (iii) over 500,000 downloads of Quantinuum’s open-sourced TKET, a world-leading quantum software development kit (SDK).
The announcements were made during Uttley’s keynote address titled, “A Measured Approach to Quantum Computing.”
These advancements are the latest examples of the company’s continued demonstration of its leadership in the quantum computing community.
“Quantinuum is accelerating quantum computing’s impact to the world,” Uttley said. “We are making significant progress with both our hardware and software, in addition to building a community of developers who are using our TKET SDK.”
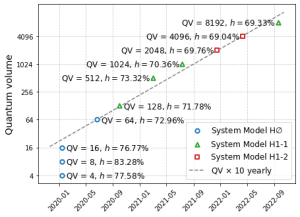
This latest quantum volume measurement of 8192 is particularly noteworthy and is the second time this year Quantinuum has published a new QV record on their trapped-ion quantum computing platform, the System Model H1, Powered by Honeywell.
A key to achieving this latest record is the new capability of directly implementing arbitrary angle two-qubit gates. For many quantum circuits, this new way of doing a two-qubit gate allows for more efficient circuit construction and leads to higher fidelity results.
Dr. Brian Neyenhuis, Director of Commercial Operations at Quantinuum, said, “This new capability allows for several user advantages. In many cases, this includes shorter interactions with the qubits, which lowers the error rate. This allows our customers to run long computations with less noise.”
These arbitrary angle gates build on the overall design strength of the trapped-ion architecture of the H1, Neyenhuis said.
“With the quantum-charged coupled device (QCCD) architecture, interactions between qubits are very simple and can be limited to a small number of qubits which means we can precisely control the interaction and don’t have to worry about additional crosstalk,” he said.
This new gate design represents a third method for Quantinuum to improve the efficiency of the H1 generation, said Dr. Jenni Strabley, Senior Director of Offering Management at Quantinuum.
“Quantinuum’s goal is to accelerate quantum computing. We know we have to make the hardware better and we have to make the algorithms smarter, and we’re doing that,” she said. “Now we can also implement the algorithms more efficiently on our H1 with this new gate design.”
A Powerful New Capability: More Information on Arbitrary Angle Gates
Currently, researchers can do single qubit gates — rotations on a single qubit — or a fully entangling two-qubit gate. It’s possible to build any quantum operation out of just those building blocks.
With arbitrary angle gates, instead of just having a two-qubit gate that’s fully entangling, scientists can use a two-qubit gate that is partially entangling.
“There are many algorithms where you want to evolve the quantum state of the system one tiny step at a time. Previously, if you wanted a tiny bit of entanglement for some small time step, you had to entangle it all the way, rotate it a little bit, and then unentangle it almost all the way back,” Neyenhuis said. “Now we can just add this tiny little bit of entanglement natively and then go to the next step of the algorithm.”
There are other algorithms where this arbitrary angle two-qubit gate is the natural building block, according to Neyenhuis. One example is the quantum Fourier transform. Using arbitrary angle two-qubit gates cuts the number of two-qubit gates (and the overall error) in half, drastically improving the fidelity of the circuit. Researchers can use this new gate design to run harder problems that resulted in catastrophic errors in previous experiments.
“By going to an arbitrary angle gate, in addition to cutting the number of two-qubit gates in half, the error we get per gate is lower because it scales with the amplitude of that gate,” Neyenhuis said.
This is a powerful new capability, particularly for noisy intermediate-scale quantum algorithms. Another demonstration from the Quantinuum team was to use arbitrary angle two-qubit gates to study non-equilibrium phase transitions, the technical details of which are available on the arXiv here.
“For the algorithms that we are going to want to run in this NISQ regime that we’re in right now, this is a more efficient way to run your algorithm,” Neyenhuis said. “There are lots of different circuits you would want to run where this arbitrary angle gate gives you a fairly significant increase in the fidelity of your overall circuit. This capability also allows for a speed up in the circuit execution by removing unneeded gates, which ultimately reduces the time of executing a job on our machines.”
Researchers working with machine learning algorithms, variational algorithms, and time evolution algorithms would see the most benefit from these new gates. This advancement is particularly relevant for simulating the dynamics of other quantum systems.
“This just gave us a big win in fidelity because we can run the sort of interaction you’re after natively, rather than constructing it out of some other Lego blocks,” Neyenhuis said.
A New Milestone in Quantum Volume
Quantum volume tests require running arbitrary circuits. At each slice of the quantum volume circuit, the qubits are randomly paired up and a complex two-qubit operation is performed. This SU(4) gate can be constructed more efficiently using the arbitrary angle two-qubit gate, lowering the error at each step of the algorithm.

The H1-1’s quantum volume of 8192 is due in part to the implementation of arbitrary angle gates and the continued reduction in error rates. Quantinuum’s last quantum volume increase was in April when the System Model H1-2 doubled its performance to become the first commercial quantum computer to pass Quantum Volume 4096.
This new increase is the seventh time in two years that Quantinuum’s H-Series hardware has set an industry record for measured quantum volume as it continues to achieve its goal of 10X annual improvement.
Quantum volume, a benchmark introduced by IBM in 2019, is a way to measure the performance of a quantum computer using randomized circuits, and is a frequently used metric across the industry.
Building a Quantum Ecosystem Among Developers
Quantinuum has also achieved another milestone: over 500,000 downloads of TKET.
TKET is an advanced software development kit for writing and running programs on gate-based quantum computers. TKET enables developers to optimize their quantum algorithms, reducing the computational resources required, which is important in the NISQ era.
TKET is open source and accessible through the PyTKET Python package. The SDK also integrates with major quantum software platforms including Qiskit, Cirq and Q#. TKET has been available as an open source language for almost a year.
This universal availability and TKET’s portability across many quantum processors are critical for building a community of developers who can write quantum algorithms. The number of downloads includes many companies and academic institutions which account for multiple users.
Quantinuum CEO Ilyas Khan said, “Whilst we do not have the exact number of users of TKET, it is clear that we are growing towards a million people around the world who have taken advantage of a critical tool that integrates across multiple platforms and makes those platforms perform better. We continue to be thrilled by the way that TKET helps democratize as well as accelerate innovation in quantum computing.”
Arbitrary angle two-qubit gates and other recent Quantinuum advances are all built into TKET.
“TKET is an evolving platform and continues to take advantage of these new hardware capabilities,” said Dr. Ross Duncan, Quantinuum’s Head of Quantum Software. “We’re excited to put these new capabilities into the hands of the rapidly increasing number of TKET users around the world.”
Additional Data for Quantum Volume 8192
The average single-qubit gate fidelity for this milestone was 99.9959(5)%, the average two-qubit gate fidelity was 99.71(3)% with fully connected qubits, and state preparation and measurement fidelity was 99.72(1)%. The Quantinuum team ran 220 circuits with 90 shots each, using standard QV optimization techniques to yield an average of 175.2 arbitrary angle two-qubit gates per circuit.
The System Model H1-1 successfully passed the quantum volume 8192 benchmark, outputting heavy outcomes 69.33% of the time, with a 95% confidence interval lower bound of 68.38% which is above the 2/3 threshold.
Source: Quantinuum




























































