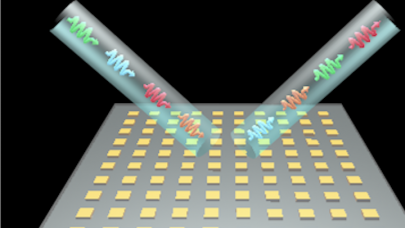
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind., July 16, 2019 — Quantum information processing promises to be much faster and more secure than what today’s supercomputers can achieve, but doesn’t exist yet because its building blocks, qubits, are notoriously unstable.
Purdue University researchers are among the first to build a gate – what could be a quantum version of a transistor, used in today’s computers for processing information – with qudits. Whereas qubits can exist only in superpositions of 0 and 1 states, qudits exist in multiple states, such as 0 and 1 and 2. More states mean that more data can be encoded and processed.
The gate would not only be inherently more efficient than qubit gates, but also more stable because the researchers packed the qudits into photons, particles of light that aren’t easily disturbed by their environment. The researchers’ findings appear in npj Quantum Information.
The gate also creates one of the largest entangled states of quantum particles to date – in this case, photons. Entanglement is a quantum phenomenon that allows measurements on one particle to automatically affect measurements on another particle, bringing the ability to make communication between parties unbreakable or to teleport quantum information from one point to another, for example.
The more entanglement in the so-called Hilbert space – the realm where quantum information processing can take place – the better.
Previous photonic approaches were able to reach 18 qubits encoded in six entangled photons in the Hilbert space. Purdue researchers maximized entanglement with a gate using four qudits – the equivalent of 20 qubits – encoded in only two photons.
In quantum communication, less is more. “Photons are expensive in the quantum sense because they’re hard to generate and control, so it’s ideal to pack as much information as possible into each photon,” said Poolad Imany, a postdoctoral researcher in Purdue’s School of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
The team achieved more entanglement with fewer photons by encoding one qudit in the time domain and the other in the frequency domain of each of the two photons. They built a gate using the two qudits encoded in each photon, for a total of four qudits in 32 dimensions, or possibilities, of both time and frequency. The more dimensions, the more entanglement.
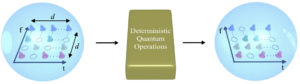
Starting from two photons entangled in the frequency domain and then operating the gate to entangle the time and frequency domains of each photon generates four fully-entangled qudits, which occupy a Hilbert space of 1,048,576 dimensions, or 32 to the fourth power.
Typically, gates built on photonic platforms to manipulate quantum information encoded in separate photons work only some of the time because photons naturally don’t interact with each other very well, making it extremely difficult to manipulate the state of one photon based on the state of another. By encoding quantum information in the time and frequency domains of photons, Purdue researchers made operating the quantum gate deterministic as opposed to probabilistic.
The team implemented the gate with a set of standard off-the-shelf equipment used daily in the optical communication industry.
“This gate allows us to manipulate information in a predictable and deterministic way, which means that it could perform the operations necessary for certain quantum information processing tasks,” said Andrew Weiner, Purdue’s Scifres Family Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, whose lab specializes in ultrafast optics.
Next, the team wants to use the gate in quantum communications tasks such as high-dimensional quantum teleportation as well as for performing quantum algorithms in applications such as quantum machine learning or simulating molecules.
The work is funded in part by the National Science Foundation (Grant number 1839191-ECCS) and a Wigner Fellowship at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Source: Kayla Wiles, Purdue University