Jan. 10, 2019 — Why are some animals committed to their mates and others are not?
According to a new study led by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin that looked at 10 species of vertebrates, evolution used a kind of universal formula for turning non-monogamous species into monogamous species — turning up the activity of some genes and turning down others in the brain.
“Our study spans 450 million years of evolution, which is how long ago all these species shared a common ancestor,” said Rebecca Young, research associate in UT Austin’s Department of Integrative Biology and first author of the study published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The authors define monogamy in animals as forming a pair bond with one mate for at least one mating season, sharing at least some of the work of raising offspring and defending young together from predators and other hazards. Researchers still consider animals monogamous if they occasionally mate with another.
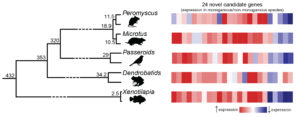
The researchers studied five pairs of closely related species – four mammals, two birds, two frogs and two fish — each with one monogamous and one non-monogamous member. These five pairs represent five times in the evolution of vertebrates that monogamy independently arose, such as when the non-monogamous meadow voles and their close relatives the monogamous prairie voles diverged into two separate species.
The researchers compared gene expression in male brains of all 10 species to determine what changes occurred in each of the evolutionary transitions linked to the closely related animals. Despite the complexity of monogamy as a behavior, they found that the same changes in gene expression occurred each time. The finding suggests a level of order in how complex social behaviors come about through the way that genes are expressed in the brain.
This study covers a broader span of evolutionary time than had been explored previously. Other studies have looked at genetic differences related to evolutionary transitions to new traits, but they typically focus on animals separated by, at most, tens of millions of years of evolution, as opposed to the hundreds of millions of years examined with this study.
“Most people wouldn’t expect that across 450 million years, transitions to such complex behaviors would happen the same way every time,” Young said.
Researchers examined gene activity across the genomes of the 10 species, using RNA-sequencing technology and tissue samples from three individuals of each species. The scientists detected gene-activity patterns across species using bioinformatics software and the Texas Advanced Computing Center’s (TACC’s) Wrangler data-intensive supercomputer. Using a software package, OrthoMCL, the team was able to arrange genes from distantly related species — such as a fish and a mammal — into groups based on sequence similarities. This allowed them to identify the common evolutionary formula that led to pair bonds and co-parenting in the five species that behave monogamously.
“Wrangler is set up with a relational database that allows individual computational steps to go back and talk to this database, and pull up the information it needs without any timeout errors,” Young said. “We’ve been able to run all of our species together on Wrangler using OrthoMCL, and at this point we haven’t even maxed out what Wrangler is capable of doing.”
According to Young, with traditional online databases she was only able to identify about 350 comparable genes across these 10 species; however, when she ran OrthoMCL on Wrangler, she identified almost 2,000 genes that are comparable across all of the species.
“This an enormous improvement from what is available,” Young said. “When you add this up across 10 species, you have an enormous amount of data. We’re starting at a minimum of 80,000 genes that we’re going to compare in all pairwise combinations for over three billion comparisons to perform and organize in total. The staff at TACC and the Wrangler supercomputer helped make this science possible.”
Supercomputer time was awarded through XSEDE, the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment, funded by the National Science Foundation.
The paper’s other UT Austin authors are senior author professor Hans Hofmann and professor Steven Phelps.
Authors at other institutions are Michael Ferkin (University of Memphis), Nina Ockendon-Powell (University of Bristol), Veronica Orr (University of California, Davis), Ákos Pogány (Eötvös Loránd University), Corinne Richards-Zawacki (University of Pittsburgh), Kyle Summers (East Carolina University), Tamás Székely (University of Bath), Brian Trainor (University of California, Davis), Araxi Urrutia (University of Bath and Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México), Gergely Zachar (Semmelweis University) and Lauren O’Connell, a former UT Austin graduate student (Stanford University).
This work was supported by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund.
Source: Faith Singer-Villalobos, TACC



























































