
Supercomputing 2023: Odds and Ends from the Show
November 20, 2023
This year's fantastic Supercomputing 2023 was back in full form. Attendees seemed to be glad that the show was back in Denver, which was a preferred destination Read more…

Forget Zettascale, Trouble is Brewing in Scaling Exascale Supercomputers
November 14, 2023
In 2021, Intel famously declared its goal to get to zettascale supercomputing by 2027, or scaling today's Exascale computers by 1,000 times. Moving forward t Read more…

Leveraging Machine Learning in Dark Matter Research for the Aurora Exascale System
September 25, 2023
Scientists have unlocked many secrets about particle interactions at atomic and subatomic levels. However, one mystery that has eluded researchers is dark matte Read more…
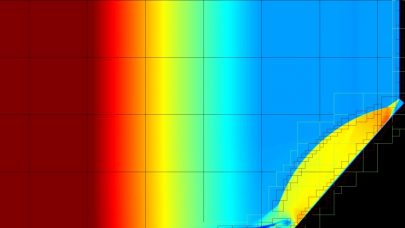
AMReX: A Performance-Portable Framework for Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Applications
August 21, 2023
Performance, portability, and broad functionality are all key features of the AMReX software framework, which was developed by researchers at Lawrence Berkeley Read more…

Top500: Frontier Gains 92 Petaflops; Henri Gets a Little Greener
May 22, 2023
It’s not quite homeostasis, but it's close. There was little movement in the latest Top500, released today from the International Supercomputing Conference (I Read more…

Q&A with ORNL’s Travis Humble, an HPCwire Person to Watch in 2023
May 12, 2023
Travis Humble is the director the Quantum Science Center (QSC) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. QSC is one of six National QIS Research established by the U.S. National Quantum Initiative Act (NQIA) in 2018 and being overseen by the Department of Energy. Hopes are high that these centers, through their own research and in collaboration... Read more…

White House Budget Request Includes Funding for Leadership-Class Computing Facility
March 10, 2023
The U.S. government is dedicating a record amount of $25 billion as part of the 2024 budget to emerging technologies as the country looks to counter the technology threat from China. The budget includes billions of dollars earmarked to boost the supercomputing infrastructure, semiconductors, and cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and quantum computing. The technology... Read more…

At ORNL, Jeff Smith Becomes Interim Director, as Search for Permanent Lab Chief Continues
January 20, 2023
UT-Battelle, which manages Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) for the U.S. Department of Energy, has appointed Jeff Smith as interim director for the lab as t Read more…

- Click Here for More Headlines

Whitepaper
Transforming Industrial and Automotive Manufacturing
In this era, expansion in digital infrastructure capacity is inevitable. Parallel to this, climate change consciousness is also rising, making sustainability a mandatory part of the organization’s functioning. As computing workloads such as AI and HPC continue to surge, so does the energy consumption, posing environmental woes. IT departments within organizations have a crucial role in combating this challenge. They can significantly drive sustainable practices by influencing newer technologies and process adoption that aid in mitigating the effects of climate change.
While buying more sustainable IT solutions is an option, partnering with IT solutions providers, such and Lenovo and Intel, who are committed to sustainability and aiding customers in executing sustainability strategies is likely to be more impactful.
Learn how Lenovo and Intel, through their partnership, are strongly positioned to address this need with their innovations driving energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Download Now
Sponsored by Lenovo
Whitepaper
How Direct Liquid Cooling Improves Data Center Energy Efficiency
Data centers are experiencing increasing power consumption, space constraints and cooling demands due to the unprecedented computing power required by today’s chips and servers. HVAC cooling systems consume approximately 40% of a data center’s electricity. These systems traditionally use air conditioning, air handling and fans to cool the data center facility and IT equipment, ultimately resulting in high energy consumption and high carbon emissions. Data centers are moving to direct liquid cooled (DLC) systems to improve cooling efficiency thus lowering their PUE, operating expenses (OPEX) and carbon footprint.
This paper describes how CoolIT Systems (CoolIT) meets the need for improved energy efficiency in data centers and includes case studies that show how CoolIT’s DLC solutions improve energy efficiency, increase rack density, lower OPEX, and enable sustainability programs. CoolIT is the global market and innovation leader in scalable DLC solutions for the world’s most demanding computing environments. CoolIT’s end-to-end solutions meet the rising demand in cooling and the rising demand for energy efficiency.
Download Now
Sponsored by CoolIT
Advanced Scale Career Development & Workforce Enhancement Center
Featured Advanced Scale Jobs:
HPCwire Resource Library
HPCwire Product Showcase
© 2024 HPCwire. All Rights Reserved. A Tabor Communications Publication
HPCwire is a registered trademark of Tabor Communications, Inc. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form or medium without express written permission of Tabor Communications, Inc. is prohibited.
























