
Volunteer Computing Project Helps Smash Childhood Cancer
February 1, 2017
On Tuesday, IBM announced that its World Community Grid will provide free virtual supercomputing power to a global team of scientists engaged in the fight again Read more…

Univa Expands Grid Engine Support for Docker and Intel KNL
May 31, 2016
Univa today announced general availability of Grid Engine 8.4.0. The latest version of Grid Engine includes many new features including expanded support for Docker containers as well as “preview support” for Intel’s latest Xeon Phi code named Knights Landing processor. Univa also reports fixing more than 80 prior issues. Leading the container enhancements, users can now automatically dispatch and run jobs in Docker containers, from a user specified Docker image. Read more…

New Storage Options Coming to Globus Users
October 27, 2015
At the SpectraSummit event in Boulder, Colorado, earlier this month, HPCwire learned of a developing partnership between storage vendor Spectra Logic and resear Read more…

Charity Engine Debuts Million-Core Challenge
February 9, 2015
Charity Engine, the volunteer computing grid operated by the Worldwide Computer Company, announced it will donate three million core-hours of computing to three Read more…
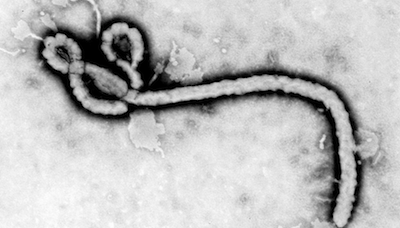
Volunteers Contribute Spare Cycles to Ebola Research
December 4, 2014
IBM announced that its World Community Grid, now "powered by its SoftLayer cloud," will provide free virtual supercomputing power to The Scripps Research Instit Read more…

Community Grid Fosters Microbial Discovery
October 22, 2014
An international team of volunteers is putting their spare computing power to work unlocking the secrets of microbes from around the world. By plugging in to Read more…

Free Market HPC Cloud In Development
August 18, 2014
Distributed computing has undergone many permutations, from its roots in grid computing to support large scientific endeavors to Sun-style utility computing, to Read more…

A Heterogeneous Approach to Molecular Dynamics
May 22, 2014
As director of the biophysics program at Stanford University, Vijay Pande understands that cloud is no replacement for supercomputers like the petascale Blue Wa Read more…

- Click Here for More Headlines

Whitepaper
Transforming Industrial and Automotive Manufacturing
In this era, expansion in digital infrastructure capacity is inevitable. Parallel to this, climate change consciousness is also rising, making sustainability a mandatory part of the organization’s functioning. As computing workloads such as AI and HPC continue to surge, so does the energy consumption, posing environmental woes. IT departments within organizations have a crucial role in combating this challenge. They can significantly drive sustainable practices by influencing newer technologies and process adoption that aid in mitigating the effects of climate change.
While buying more sustainable IT solutions is an option, partnering with IT solutions providers, such and Lenovo and Intel, who are committed to sustainability and aiding customers in executing sustainability strategies is likely to be more impactful.
Learn how Lenovo and Intel, through their partnership, are strongly positioned to address this need with their innovations driving energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Download Now
Sponsored by Lenovo
Whitepaper
How Direct Liquid Cooling Improves Data Center Energy Efficiency
Data centers are experiencing increasing power consumption, space constraints and cooling demands due to the unprecedented computing power required by today’s chips and servers. HVAC cooling systems consume approximately 40% of a data center’s electricity. These systems traditionally use air conditioning, air handling and fans to cool the data center facility and IT equipment, ultimately resulting in high energy consumption and high carbon emissions. Data centers are moving to direct liquid cooled (DLC) systems to improve cooling efficiency thus lowering their PUE, operating expenses (OPEX) and carbon footprint.
This paper describes how CoolIT Systems (CoolIT) meets the need for improved energy efficiency in data centers and includes case studies that show how CoolIT’s DLC solutions improve energy efficiency, increase rack density, lower OPEX, and enable sustainability programs. CoolIT is the global market and innovation leader in scalable DLC solutions for the world’s most demanding computing environments. CoolIT’s end-to-end solutions meet the rising demand in cooling and the rising demand for energy efficiency.
Download Now
Sponsored by CoolIT
Advanced Scale Career Development & Workforce Enhancement Center
Featured Advanced Scale Jobs:
HPCwire Resource Library
HPCwire Product Showcase
© 2024 HPCwire. All Rights Reserved. A Tabor Communications Publication
HPCwire is a registered trademark of Tabor Communications, Inc. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form or medium without express written permission of Tabor Communications, Inc. is prohibited.
























