July 27, 2023 — For decades, scientists have been trying to solve the mystery of what makes quantum computers more powerful than classical computers. The origins of this quest can be traced all the way to Albert Einstein who famously called quantum mechanical entanglement “spooky action at a distance”. Now in a groundbreaking paper published in the Physical Review Letters, a team of scientists led by Assistant Professor William Fefferman from the University of Chicago’s Department of Computer Science have found a computational problem in which entanglement is directly responsible for a dramatic quantum computational speedup over any efficient classical algorithm.

Fefferman, along with lead Ph.D. student Soumik Ghosh, IBM researcher Abhinav Deshpande (who Fefferman co-advised at the University of Maryland), University of Maryland postdoc Dominik Hangleiter and University of Maryland/NIST researcher Alexey Gorshkov, debuted a problem in their paper titled “Complexity phase transitions generated by entanglement” that pinpoints two things: there is a provable quantum speedup over any classical computer, and entanglement is causing the speedup in this particular problem.
Since the early 90’s, we have had theoretical evidence that quantum computers can solve problems that are too difficult for today’s classical computers. One specific example that scientists continue to look at is Shor’s algorithm, which says quantum computers can take incredibly large numbers (think ten billion) and quickly break them into their prime factors. The foundations of modern cryptography that we use on the Internet is based on this being a hard problem to solve; so if large scale quantum computers are built, then the basis of cryptography as we know it would be compromised.
However, Shor’s algorithm is still a theoretical result because large enough and perfect enough quantum computers have not yet been built.
“Right now we are in the era of NISQ — which stands for noisy intermediate scale quantum computing,” said Ghosh. “Some companies have designed certain types of quantum computers, but one defining feature is that they are a bit noisy. Today’s quantum computers are believed to be just slightly more powerful than our best classical computers, so it’s becoming more significant to sharpen that boundary between the two.”
In the same way that classical computers are made up of bits, quantum computers are made of individual components called qubits. As Ghosh explained, today’s qubits are noisy, making them too imperfect to be efficient. A quantum computer would need hundreds of thousands of noiseless qubits to solve the near-impossible problems facing modern computers. While places like UChicago are making strides toward building large scale quantum computers that can test these theories, we don’t currently have devices capable of doing so.
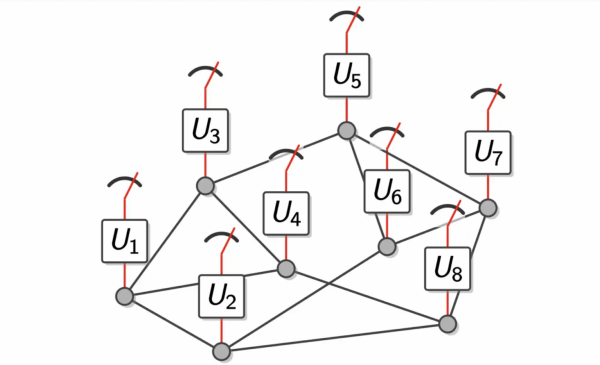
There is still plenty that scientists don’t understand about the basic foundations of quantum computing that make it hard to move forward in the field. From a first principle standpoint, certain questions need to be answered: Why is quantum computing so powerful? Why does Shor’s algorithm work? What quantum properties is it using that causes these speedups? After years of research attempting to better understand these issues, this work gives an example of a quantum system for which entanglement can be identified as the clearcut answer.
“Entanglement is a fundamental property of quantum systems, and it’s a property that we think is very different from anything that happens in the classical world,” Fefferman explained. “Furthermore, there’s always been an intuition that entanglement is one of the root causes of these quantum speedups. It’s an important contributor to the power of quantum computers, but it wasn’t totally clear that entanglement was the sole cause. That’s what our paper is trying to address.”
Entanglement is a complex and largely misunderstood phenomenon that scientists have been trying to understand for the last hundred years. Einstein, for instance, was troubled by entanglement and died trying to give a classical explanation. In essence, if you have two entangled quantum particles that are separated by a distance, no matter how far, what happens to one particle can simultaneously affect the behavior of the other particle. Abstractly, if you have a large number of particles– or qubits as the basic unit of quantum information– and you want to understand the state of this entire system, the idea of entanglement implies you won’t get any real information by looking at just one qubit; you have to look at the interactions between all of the qubits to understand the state of subsets within the system.

The problem the team presented in the paper is not useful in the same sense that Shor’s algorithm is, but it can be mathematically described and is meaningful to quantum theory. The key point is that entanglement can be seen to be the root cause of the computational speedup.
“We can talk about the same computational problem with a little bit of entanglement, and then a little bit more, and so on,” said Fefferman. “The exciting part is that when this entanglement reaches a certain threshold, we go from an easy problem for a classical computer to a provably hard problem. Entanglement seems to be causing the increased difficulty and quantum speedup. We’ve never been able to show that in a problem like Shor’s algorithm.”
This research is part of the first steps in the broader context of pinpointing quantum speedups.
“The next step is trying to generalize this toy model to more practical systems of quantum computation,” said Ghosh. “We want to be able to understand what is causing speedups for the types of quantum computers that people are designing in real life and the type of processes that will be run using those computers.”
Source: UChicago